This article illustrates how you can store data for time-travel queries in a compressed format using Invantive UniversalSQL. The algorithm works for any type of data of any source such as Salesforce, Exact Online or Visma.net. It is based upon the Oracle-based data vault technology of Invantive Producer and suitable for use with medium-sized data sets. For data sets exceeding 100.000 rows more advanced technologies such as Invantive Producer or Invantive Data Vault are recommended.
The instructions apply for storage of the data in memory or in SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL or PostgreSQL. To use the instructions below for another storage than in-memory, please define an additional data container in your database like ‘sqlserver’ and replace history@inmemorystorage by history@sqlserver.
Instructions
Follow the steps below to store data for time-travel using Invantive UniversalSQL:
- test data;
- create history table;
- register new version;
- use.
Test Data
In this step we will create a number of versions of the same data set, each reflecting a different points-in-time. For this example, we are using a very simple invoice table.
The version at time t=0 of invoices has no contents. The version at time t=1 has the following contents:
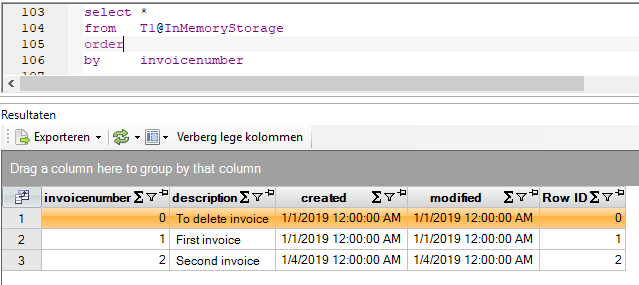
Whereas version at t=2 has the following contents:

Between t=0 and t=1, three invoices have been created. Between t=1 and t=2, the user has removed the invoice with number 0, created a new invoice 3 and updated the description of invoice 1 from “First invoice” to “New first invoice; fixed typo.”
The following code creates the test data set:
--
-- Set up data.
--
begin
create or replace table t1@inmemorystorage
as
select cast(0 as int32) invoicenumber
, 'To delete invoice' description
, to_date('20190101', 'YYYYMMDD') created
, to_date('20190101', 'YYYYMMDD') modified
union all
select cast(1 as int32) invoicenumber
, 'First invoice' description
, to_date('20190101', 'YYYYMMDD') created
, to_date('20190101', 'YYYYMMDD') modified
union all
select cast(2 as int32) invoicenumber
, 'Second invoice' description
, to_date('20190104', 'YYYYMMDD') created
, to_date('20190104', 'YYYYMMDD') modified
;
create or replace table t0@inmemorystorage
as
select *
from t1@InMemoryStorage
where false
;
create or replace table t2@InMemoryStorage
as
--
-- New situation contains all old invoices except the
-- first invoice which was changed, and invoice 0 which
-- was deleted, plus one new invoice.
--
select * except rowid$
from t1@inmemorystorage
where invoicenumber not in (0, 1)
union all
--
-- Changed invoice 1.
--
select invoicenumber
, 'New first invoice; fixed typo.' description
, created
, to_date('20190212', 'YYYYMMDD') modified
from t1@InMemoryStorage
where invoicenumber = 1
union all
select cast(3 as int32) invoicenumber
, 'Third invoice' description
, to_date('20190312', 'YYYYMMDD') created
, to_date('20190312', 'YYYYMMDD') modified
;
end;
Create History Table
All historical and current records are stored in a table hist@inmemorystorage. This table contains all columns contained with the original data set. Additionally, it has columns recognizable by the prefix ‘h_’ to enable time-travel:
- h_id: an ever-increasing number over time.
- h_date_start_utc: the effective start date of the row (UTC).
- h_date_end_utc: the effective end date of the row (exclusive) (UTC). The date December 31, 9999 is used to a record without end to enable index use.
- h_is_last_known: a signal that indicates whether the row is relevant for the last known situation.
- h_event: an audit column that registers the event, being either ‘I’ for ‘Insert’, ‘U’ for ‘Update’ and ‘D’ for ‘Delete’.
- h_session_id: an audit column that registers the Invantive UniversalSQL session.
- h_created_on: an audit column that registers the device used.
- h_created_by: an audit column that registers the name of the user.
- h_date_measured_utc: an audit column that registers the moment in time (UTC) at which history was updated.
The following code creates the history table and should be executed once:
--
-- Initial setup of history table "hist".
--
begin
if not exists (select /*+ ods(false) */ 1 from systemtables@datadictionary where name = 'HIST')
then
create or replace table hist@inmemorystorage
as
select cast(0 as int64) h_id label 'ID'
, sys_context('USERENV', 'SESSIONID') h_session_id label 'Measurement Session ID'
, sys_context('USERENV', 'CLIENT_MACHINE_NAME') h_created_on label 'Machine Created on'
, sys_context('USERENV', 'USER_FULL_NAME') h_created_by label 'User Created by'
, cast(sysdateutc as datetime) h_date_measured_utc label 'Measured (UTC)'
, cast(sysdateutc as datetime) h_date_start_utc label 'Start Date (UTC)'
, cast(sysdateutc as datetime) h_date_end_utc label 'End Date (UTC)'
, cast('X' as char) h_event label 'Event'
, cast(true as boolean) h_is_last_known label 'Last Known State?'
, t.* except rowid$
from t0@inmemorystorage t
where false
;
end if;
end;
Register new Version in History
The registration of a new (differential) version in the history table consists of three steps:
- determine last ID used to number the history records;
- load changes between versions;
- complete previously current records.
These three steps should be executed once after running
For the test, you can create the old and new situation using the following statements to make old equal t=0 and new the situation at t=1:
create or replace table OLD@InMemoryStorage
as
select *
from t0@inmemorystorage
create or replace table NEW@InMemoryStorage
as
select *
from t1@inmemorystorage
And then one more time after moving old and new to t=1 and t=2 respectively:
create or replace table OLD@InMemoryStorage
as
select *
from t1@inmemorystorage
create or replace table NEW@InMemoryStorage
as
select *
from t2@inmemorystorage
Determine last ID Used
The following query for use with Invantive Data Hub or Invantive Query Tool stores the last used ID in the local variable H_ID_LAST:
select cast(coalesce(h_id_max, 0) as int64) h_id_max_nn
from ( select /*+ ods(false) */
max(h_id) h_id_max
from hist@InMemoryStorage
)
local define H_ID_LAST "${outcome:0,0}"
The hint of ods(false) can be removed when not running in combination with Invantive Data Replicator.
On initial use, the last ID used will be 0. On continuing use, higher numbers will be returned.
Load Changes between Versions
Then, a range of changes between the previous and current version is loaded into the history table using:
--
-- Take list of result sets (with partition column) and change them into time travel list.
--
insert
into hist@inmemorystorage
select cast(to_number('${H_ID_LAST}') + row_number() as int64) h_id
, sys_context('USERENV', 'SESSIONID') h_session_id
, sys_context('USERENV', 'CLIENT_MACHINE_NAME') h_created_on
, sys_context('USERENV', 'USER_FULL_NAME') h_created_by
, sysdateutc h_date_measured_utc
, t.*
from ( select created + (sysdateutc - sysdate) h_date_start_utc
, to_date('99991231', 'YYYYMMDD') h_date_end
, 'I' h_event
, true h_is_last_known
, new.* except rowid$
from new@InMemoryStorage new
where cast(new.invoicenumber as varchar2)
not in
( select cast(invoicenumber as varchar2)
from old@InMemoryStorage
)
union all
select sysdateutc h_date_start_utc
, sysdateutc h_date_end_utc
, 'D' h_event
, false h_is_last_known
, old.* except rowid$
from old@InMemoryStorage old
where cast(old.invoicenumber as varchar2)
not in
( select cast(invoicenumber as varchar2)
from new@InMemoryStorage
)
union all
select new.modified + (sysdateutc - sysdate) h_date_start_utc
, to_date('99991231', 'YYYYMMDD') h_date_end_utc
, 'U' h_event
, true h_is_last_known
, new.* except rowid$
from new@InMemoryStorage new
join old@InMemoryStorage old
on old.invoicenumber = new.invoicenumber
--
-- Rewrite this clause to a compare on all fields when no modified is available or not covering all scenarios.
--
and old.modified != new.modified
) t
Complete Previously Current Records
After loading the new data, the previously current history records must be marked as ended. This is done using a piece of Invantive PSQL:
begin
for r
in
( select /*+ ods(false) */ h_id
, h_date_start_utc
, invoicenumber
from hist@inmemorystorage
where h_id
in
( select /*+ ods(false) */ max(h_id)
from hist@InMemoryStorage
group
by invoicenumber
)
)
loop
--
-- Update old records to be no longer last known.
--
update hist@inmemorystorage
set h_is_last_known = false
where h_is_last_known = true
and invoicenumber = r.invoicenumber
and h_id != r.h_id
;
--
-- Put an end date on records now no longer current.
--
update hist@inmemorystorage
--
-- No 1 second offset as on Oracle with Invantive Producer,
-- since Invantive UniversalSQL optimizes this better.
--
-- Use MOMENT >= start and MOMENT < end
--
set h_date_end_utc = r.h_date_start_utc
where h_date_end_utc = to_date('99991231', 'YYYYMMDD')
and invoicenumber = r.invoicenumber
and h_id != r.h_id
;
end loop;
end;
Using the History
Full History
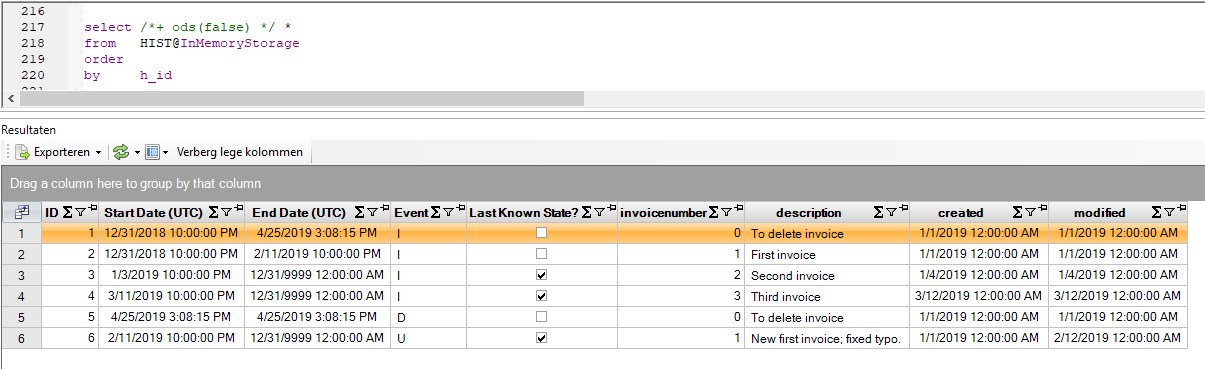
The relevant contents of the history table after executing the steps above are:
For example, you can see for invoice number 1 that starting December 31, 2018 10 PM (UTC) the description was “First invoice”. This description lasted till February 11, 2019 10 PM (UTC) when it was changed to “New first invoice; fixed typo.” This description is still current.
Current Records
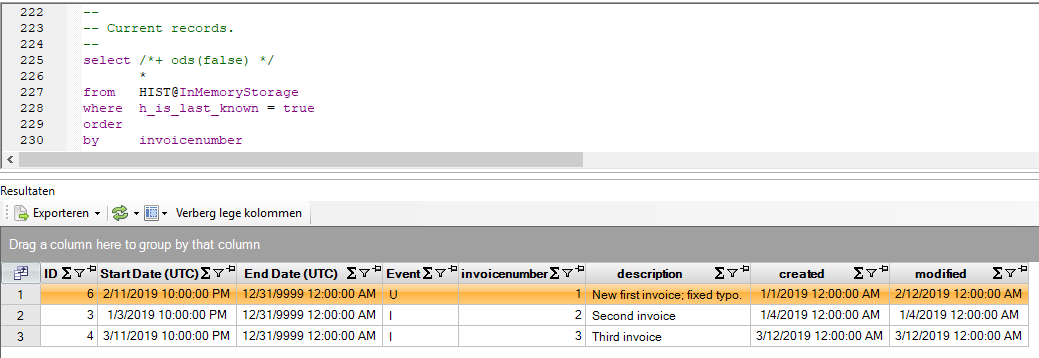
You can retrieve the last known or current records by querying on the last known signal:
Contents at Moment in Time
You can also easily reconstruct the registered history for a specific moment in time, using a query such as:
Enable Power BI Slider with a Where Clause
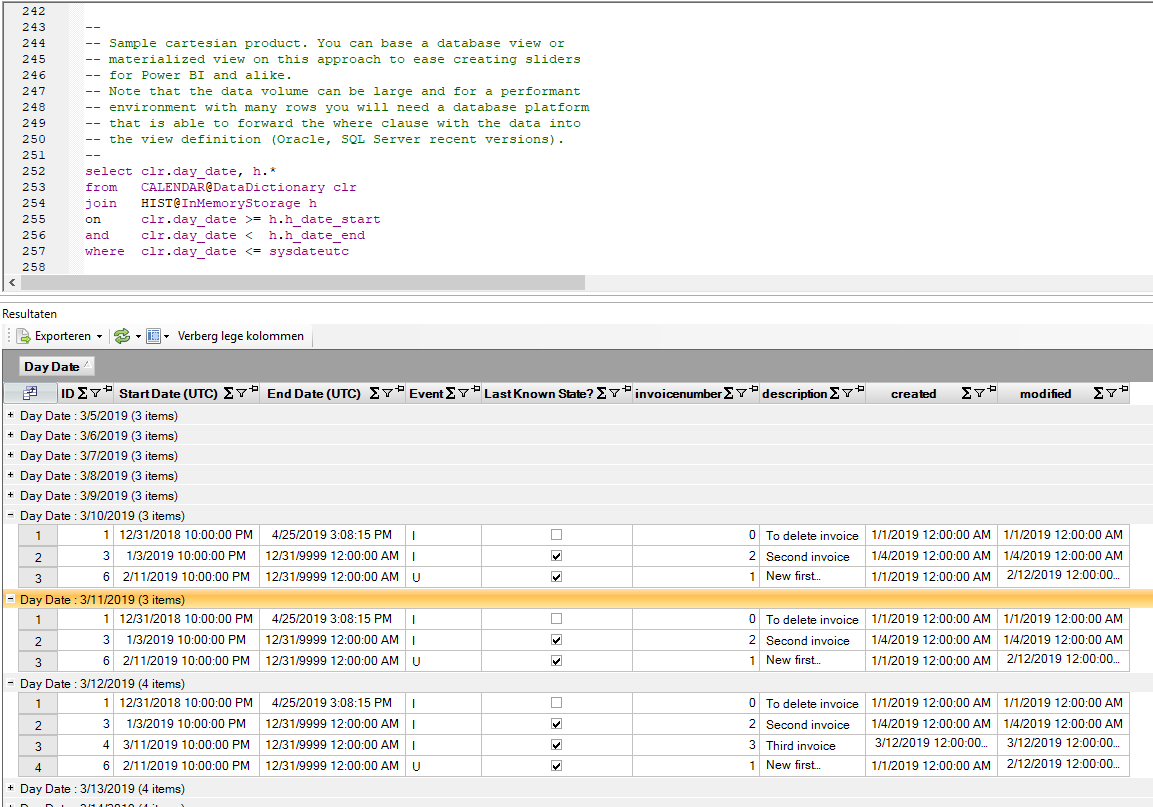
A popular use of this historical is to add a slider to a Power BI report. The slider generates a where clause to an SQL statement on a table or view. However, compared to “Contents at Moment in Time” this requires that a single date can be filtered upon. Using a Carthesian product of a calendar view and the historical data, you can easily generate such functionality using a view or materialized view with a query as shown below. Please remember to replace the Calendar@datadictionary table by the calendar view of your platform or environment.
In the sample below you can see that there are no differences when moving from March 10 to March 11, 2019. However, going to March 12, 2019, an additional records is added for the invoice with number 3.
Use on a Database
The code presented can be used without essential changes by replacing hist@inmemorystorage by hist@sqlserver or another alias. However, remember that old@inmemorystorage table is not available across sessions. You can either use Ossus or your database to memorize the current situation to load old@inmemorystorage on a later run for.
For example, after the PSQL block, you could add:
create or replace table old@PERSISTENTSTORAGE
as
select /*+ ods(false) */
*
from old@inmemorystorage
And then replace the create table of old@inmemorystorage by:
create or replace table old@inmemorystorage
as
select *
from old@PERSISTENTSTORAGE
And replace the create table of new@inmemorystorage by:
create or replace table new@inmemorystorage
as
select *
from exactonlinerest..salesinvoices
On the last query, you can choose whether to take an up-to-date replica using the hint:
/*+ ods(true, interval '1 seconds') */
which possibly might use incremental loading such as with webhooks, or to use a normal download of the data using the hint:
/*+ ods(false) */
Remove Update
Some database platforms are less well-suited for handling updates. For instance PostgreSQL and Teradata have been designed for insert and delete performance.
You can remove the updates from the algorithm by removing the last active signal and end date at the expense of slightly less query performance.